Embarking on your investment journey can feel daunting, especially as a beginner. The sheer volume of options and potential risks can be paralyzing. But fear not! 2024 presents several low-risk investment avenues perfectly suited for those taking their first steps into the world of finance. This guide navigates the landscape of safe and steady growth, providing a clear understanding of options like high-yield savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), government bonds, and Series I savings bonds.
We’ll explore the nuances of each, helping you build a portfolio tailored to your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Understanding your risk tolerance is paramount. Are you comfortable with minimal fluctuations in your investment value, prioritizing capital preservation? Or are you willing to accept slightly higher risk for potentially greater returns? This guide will help you determine your risk profile and match it with appropriate investment strategies. We’ll delve into the mechanics of each option, comparing interest rates, fees, and potential returns, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
We will also address the ever-present factor of inflation and how to mitigate its impact on your savings. By the end, you’ll possess a solid foundation for building a diversified, low-risk portfolio that aligns with your aspirations.
Understanding Risk Tolerance for Beginners
Investing involves navigating the inherent uncertainty of market fluctuations. A crucial element in successful investing, particularly for beginners, is understanding and managing your risk tolerance. This refers to your comfort level with the possibility of losing some or all of your invested capital in pursuit of higher returns. A well-defined risk tolerance guides investment choices, ensuring they align with your financial goals and emotional capacity.
Ignoring your risk tolerance can lead to impulsive decisions and potentially significant financial setbacks.
Risk Tolerance Assessment
Accurately assessing your risk tolerance is paramount before making any investment decisions. This self-assessment helps you categorize your comfort level with potential losses, allowing you to select appropriate investment strategies. A higher risk tolerance suggests a greater willingness to accept potential losses for the chance of higher returns, while a lower risk tolerance prioritizes capital preservation over potentially higher gains.
The following questionnaire offers a preliminary assessment.
Risk Tolerance Questionnaire
Consider each statement and select the option that best reflects your feelings:
- Statement 1: I am comfortable with the possibility of losing some of my investment in exchange for potentially higher returns.
a) Strongly Disagree b) Disagree c) Neutral d) Agree e) Strongly Agree - Statement 2: I prefer investments with a history of stable, predictable returns, even if they offer lower growth potential.
a) Strongly Agree b) Agree c) Neutral d) Disagree e) Strongly Agree - Statement 3: Market volatility (ups and downs) makes me nervous and I prefer to avoid it as much as possible.
a) Strongly Agree b) Agree c) Neutral d) Disagree e) Strongly Agree - Statement 4: I am willing to hold my investments for a longer period, even if their value fluctuates in the short term.
a) Strongly Disagree b) Disagree c) Neutral d) Agree e) Strongly Agree - Statement 5: I am prepared to experience short-term losses if it means potentially higher returns in the long term.
a) Strongly Disagree b) Disagree c) Neutral d) Agree e) Strongly Agree
Scoring: Assign numerical values to each response (Strongly Disagree = 1, Disagree = 2, Neutral = 3, Agree = 4, Strongly Agree = 5). Sum the scores for all statements. A higher total score indicates a higher risk tolerance.
Risk Tolerance Profiles and Investment Strategies
Understanding your risk tolerance score allows you to align your investment approach with your comfort level. Different risk tolerance profiles necessitate distinct investment strategies.
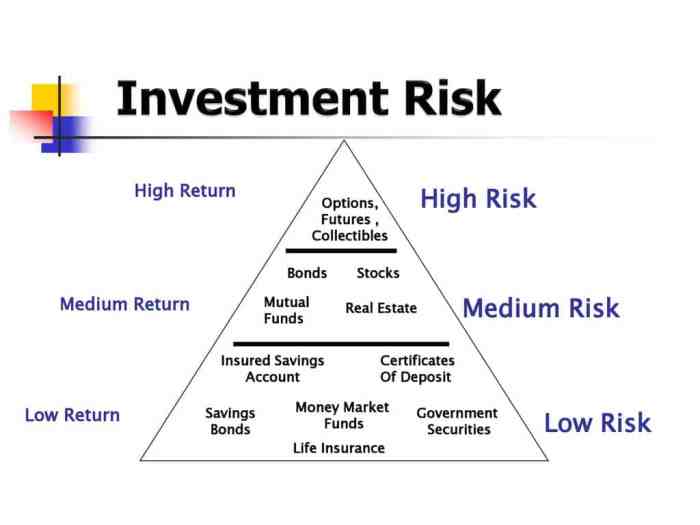
For instance, individuals with a low risk tolerance (lower total score) typically favor capital preservation. Suitable strategies include high-yield savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and government bonds. These options generally offer lower returns but present minimal risk of principal loss. The focus is on stability and security.
Conversely, those with a high risk tolerance (higher total score) may consider investments like individual stocks, small-cap funds, or emerging market funds. While these offer the potential for significant returns, they also carry a substantially higher risk of loss. This strategy is suitable for long-term investors who can withstand market fluctuations and are comfortable with the possibility of short-term losses.
Moderate risk tolerance profiles often benefit from a diversified portfolio, incorporating a mix of lower-risk and higher-risk investments. This approach aims to balance the potential for growth with the need for capital preservation. A diversified portfolio might include a combination of bonds, stocks, and real estate investment trusts (REITs).
High-Yield Savings Accounts and Money Market Accounts
For beginners navigating the world of low-risk investments in 2024, high-yield savings accounts (HYSA) and money market accounts (MMA) offer attractive options for building wealth while preserving capital. Both provide FDIC insurance (up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, for each account ownership category) offering a safety net against potential bank failures, a crucial factor for risk-averse investors.
Understanding their nuances is key to selecting the best fit for individual financial goals.
These accounts differ primarily in their features and the level of access to funds. Both offer competitive interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, providing a better return on your deposited funds than simply keeping money in a checking account. However, the interest earned is subject to federal and possibly state income tax. This tax liability should be factored into any investment decisions.
High-Yield Savings Account Features and Benefits
High-yield savings accounts are designed for easy access to funds while earning a higher interest rate than traditional savings accounts. They typically offer online access, allowing for convenient account management and transfers. The ease of access and liquidity makes them ideal for emergency funds or short-term savings goals. Features often include debit cards for ATM withdrawals (though this may affect interest rates offered), mobile banking apps for account monitoring, and automatic transfers for building savings.
The higher interest rates are a significant advantage, offering a better return on your money compared to standard savings accounts. However, it’s crucial to remember that interest rates are variable and can fluctuate based on market conditions.
Money Market Account Features and Benefits
Money market accounts offer a blend of savings and checking account features. They often provide higher interest rates than standard savings accounts and may allow a limited number of checks or debit card transactions per month. MMAs typically require a higher minimum balance than HYSA, but in return, they might offer additional perks such as debit cards, check-writing capabilities, and potentially higher interest rates than comparable HYSA options.
The higher minimum balance requirement can be a barrier for some beginners, but the potential for higher returns and added features can make them worthwhile for those who meet the criteria.
High-Yield Savings Accounts vs. Money Market Accounts: A Comparison
While both HYSA and MMA offer competitive interest rates and FDIC insurance, key differences exist. HYSA prioritizes accessibility and ease of use, making them ideal for emergency funds. MMAs, while offering similar FDIC insurance and higher rates, often come with higher minimum balance requirements and may provide additional features like check writing, although this might come with transaction limits.
The choice between the two depends largely on individual financial needs and risk tolerance. Individuals needing frequent access to funds will likely prefer a HYSA, while those with larger balances and less need for immediate access might find an MMA more beneficial.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a High-Yield Savings Account or Money Market Account
Several factors should be carefully considered when selecting a HYSA or MMA. Interest rate is paramount; higher rates directly translate to greater returns. However, it’s essential to compare rates across multiple institutions, as they fluctuate regularly. Minimum balance requirements vary significantly, impacting accessibility. Some accounts might impose monthly fees if the minimum balance isn’t maintained.
Finally, the convenience of access, including online and mobile banking features, plays a crucial role in user experience.
Interest Rates, Minimum Balances, and Fees: A Comparison
The following table provides a snapshot of potential interest rates, minimum balance requirements, and fees for several hypothetical examples. Remember that these are examples only and actual rates and fees vary widely depending on the financial institution and prevailing market conditions. It’s crucial to check directly with each institution for the most up-to-date information.
| Account Type | Institution | Interest Rate (APY) | Minimum Balance | Monthly Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HYSA | Example Bank A | 4.00% | $0 | $0 |
| HYSA | Example Bank B | 3.75% | $100 | $5 (if balance below $1000) |
| MMA | Example Bank C | 4.25% | $1000 | $0 |
| MMA | Example Bank D | 4.00% | $2500 | $10 (if balance below $5000) |
Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) represent a foundational low-risk investment option, particularly well-suited for beginners seeking a secure place to park their savings and earn interest. Understanding how CDs function and the various types available is crucial for making informed financial decisions. They offer a predictable return, making them a valuable tool for achieving specific financial goals.CDs operate on a straightforward principle: you deposit a lump sum of money into a bank or credit union for a fixed period, and in return, you receive a predetermined interest rate.
This interest is typically compounded, meaning you earn interest not only on your principal but also on the accumulated interest. At the end of the term, you receive your principal plus the accumulated interest. This fixed-term structure provides a degree of certainty not found in many other investment vehicles.
CD Types and Terms
The interest rate offered on a CD is directly tied to its term length – the longer you commit your money, the higher the potential interest rate. Several types of CDs cater to different investment timelines and risk tolerances. For instance, short-term CDs, typically ranging from three months to one year, offer lower interest rates but greater liquidity.
Conversely, long-term CDs, spanning several years, may offer significantly higher interest rates but come with reduced flexibility. Another type, the bump-up CD, allows for an increase in the interest rate during the term if market rates rise, offering a potential upside while still maintaining the security of a fixed-term investment. Finally, callable CDs allow the issuing institution to redeem the CD before maturity, offering them flexibility but introducing a risk for the investor of receiving their principal back sooner than expected.
CD Risks and Mitigation
While CDs are considered low-risk, they are not entirely without risk. Inflation erosion is a key concern; if inflation rises faster than the CD’s interest rate, the real return on your investment diminishes. Furthermore, the interest rate offered on a CD is fixed at the time of purchase, meaning you might miss out on higher rates if interest rates increase after you’ve opened your CD.
To mitigate these risks, investors should carefully consider the current inflation rate and interest rate forecasts when choosing a CD term and rate. Diversifying investments across multiple CDs with varying terms can also help to reduce overall risk.
Early Withdrawal Penalties
A significant consideration with CDs is the penalty for early withdrawal. Most CDs impose a penalty – typically a loss of several months’ worth of interest – if you withdraw your money before the maturity date. The exact penalty varies depending on the institution and the specific CD terms. This penalty is designed to discourage early withdrawals and protect the institution from losses associated with early termination.
Therefore, before investing in a CD, it is crucial to understand the specific early withdrawal penalty and ensure it aligns with your financial plans and risk tolerance. Only invest in a CD if you are confident you can leave the money untouched until the maturity date. Understanding the penalty structure allows for a more informed decision-making process.
Government Bonds and Treasury Bills
Government bonds and Treasury bills represent a cornerstone of low-risk investment strategies, particularly appealing to beginners seeking stability and capital preservation. These debt instruments, issued by governments, offer a relatively predictable return and a lower risk profile compared to stocks or corporate bonds, making them a suitable component of a diversified portfolio. Understanding their characteristics and the process of purchasing them is crucial for navigating this aspect of the investment landscape.Government bonds and Treasury bills are debt securities issued by a government to finance its spending.
Treasury bills, often referred to as T-bills, are short-term debt instruments, typically maturing in less than a year. Government bonds, on the other hand, represent long-term debt obligations, with maturities ranging from several years to decades. Both are considered low-risk investments because the issuing government is backed by the full faith and credit of the nation. This means that the likelihood of default—the government failing to repay the debt—is exceptionally low, particularly for established economies like the United States.
However, it’s important to note that while the risk of default is low, the value of the bond can fluctuate based on interest rate changes in the market. Rising interest rates can decrease the value of existing bonds, although this is mitigated by holding the bond until maturity.
Risk Levels and Potential Returns
The risk associated with government bonds and Treasury bills is generally considered lower than that of other investment options such as stocks or corporate bonds. This is because the backing of a government significantly reduces the risk of default. However, the potential returns are also typically lower. Treasury bills generally offer lower returns than government bonds due to their shorter maturity periods.
Compared to high-yield savings accounts or certificates of deposit (CDs), government bonds and Treasury bills may offer slightly higher returns, but this comes with the trade-off of a longer lock-up period (for bonds). The return on these investments is directly related to the prevailing interest rates at the time of purchase and the maturity date. For example, if interest rates rise after you purchase a bond, the value of your bond may decrease, although this is not the case if you hold the bond until maturity.
Purchasing Government Bonds and Treasury Bills
Purchasing government bonds and Treasury bills can be done through several channels. One common method is through a TreasuryDirect account, a government-run website that allows direct investment in U.S. Treasury securities. This offers a streamlined and cost-effective way to purchase these instruments. Alternatively, investors can purchase these securities through brokerage firms.
Brokerage firms typically charge commissions or fees, which can vary based on the firm and the transaction size. The process typically involves creating an account with the chosen platform, selecting the desired securities (specifying the maturity date and amount), and providing payment information. Once the purchase is processed, the securities are added to the investor’s account.
Where to Purchase Government Bonds and Treasury Bills
The primary avenue for purchasing U.S. Treasury securities directly from the government is through TreasuryDirect.gov. This website provides a user-friendly interface for managing your investments. However, many brokerage firms also offer access to a broad range of government bonds and Treasury bills. These firms often provide additional services such as investment advice and portfolio management, but this usually comes with associated fees.
It’s essential to compare fees and services offered by different brokerage firms before making a decision. The choice between purchasing directly through TreasuryDirect or using a brokerage firm depends on individual preferences and investment needs. Some investors prefer the direct approach for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while others find the additional services offered by brokerage firms valuable.
Series I Savings Bonds
Series I savings bonds, often called I bonds, offer a unique investment strategy for beginners seeking low-risk growth with inflation protection. Unlike many other low-risk options, I bonds adjust their interest rate to account for inflation, providing a buffer against the erosion of purchasing power. This makes them an attractive choice for long-term savers aiming to preserve their capital’s value.Series I bonds earn interest based on two components: a fixed rate and an inflation rate.
The fixed rate remains constant for the life of the bond, while the inflation rate adjusts semi-annually based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI). This dual-rate structure provides a degree of stability and protection against rising prices.
Inflation Protection in Series I Savings Bonds
The inflation rate component of an I bond’s interest is what sets it apart from other low-risk investments. The U.S. Treasury Department calculates this rate based on changes in the CPI-U (Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers). Every six months, the Treasury recalculates the inflation rate, and this new rate is applied to the bond’s principal for the next six months.
This means your bond’s interest accrues at a rate that reflects the current inflation rate, helping to maintain your purchasing power. For example, if inflation rises significantly, the interest earned on your I bond will also increase, protecting your investment from the effects of inflation. Conversely, if inflation decreases, the interest rate will adjust accordingly. This dynamic rate ensures that your investment keeps pace with the rising cost of living, making it a valuable tool in managing long-term financial goals.
Limitations and Potential Drawbacks of Series I Savings Bonds
While I bonds offer valuable inflation protection, they also come with some limitations. One key drawback is the limited liquidity. You can’t easily cash out I bonds before a certain period, typically one year, and early withdrawal penalties apply if redeemed before five years. Furthermore, while the inflation-adjusted rate offers protection against inflation, the fixed rate component is relatively low compared to other higher-risk investments.
This means your returns may not be as substantial as those from riskier options, especially during periods of low inflation. Finally, the annual purchase limit restricts the amount an individual can invest in I bonds each year, potentially limiting their potential for substantial growth.
Purchasing Series I Savings Bonds: A Step-by-Step Guide
Acquiring Series I bonds is a straightforward process, primarily done through TreasuryDirect.gov. First, you’ll need to create a TreasuryDirect account, providing necessary personal information for verification. Once your account is set up, you can navigate to the I bond purchase section of the website. Next, you’ll specify the amount you wish to purchase (within the annual limit).
Finally, you’ll review your order and confirm the purchase. The bonds are then electronically registered in your TreasuryDirect account, eliminating the need for physical certificates. The entire process is online and generally efficient, offering a convenient way to diversify your portfolio with this inflation-protected investment option.
Diversification and Portfolio Building
Diversification is a cornerstone of sound investment strategy, particularly for beginners aiming to minimize risk. It involves spreading investments across different asset classes, reducing the impact of poor performance in any single area. This principle, rooted in the statistical concept of reducing portfolio variance, is crucial for achieving long-term financial goals while mitigating potential losses. By diversifying, investors essentially hedge against unforeseen events impacting specific sectors or asset types.The core concept behind diversification lies in the fact that different asset classes often exhibit low or negative correlation.
This means that when one asset performs poorly, another may perform well, or at least remain stable, thereby stabilizing overall portfolio returns. This principle is not merely theoretical; decades of financial market data strongly support the benefits of diversification in reducing risk.
Diversified Low-Risk Investment Portfolios for Beginners
A well-diversified low-risk portfolio typically includes a mix of highly liquid and relatively stable assets. Examples of such portfolios can vary based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals. However, a common approach involves combining several low-risk options discussed previously. For instance, a portfolio might include a mix of high-yield savings accounts, short-term Certificates of Deposit (CDs), and government bonds.
The specific allocation will depend on the investor’s time horizon and financial objectives.
Example of a Diversified Low-Risk Portfolio
Consider a hypothetical $10,000 portfolio designed for a beginner with a low-risk tolerance and a medium-term investment horizon (5-7 years). A possible allocation could be:
| Asset Class | Allocation | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| High-Yield Savings Account | $3,000 (30%) | Provides liquidity and readily accessible funds. |
| Short-Term Certificates of Deposit (CDs) | $3,000 (30%) | Offers slightly higher returns than savings accounts with a fixed term. |
| Government Bonds (Treasury Bills) | $4,000 (40%) | Provides stability and relatively low risk, backed by the government. |
This example demonstrates a diversified approach, spreading risk across different low-risk instruments. The high proportion allocated to savings accounts and CDs ensures liquidity, while government bonds provide a longer-term, slightly higher return component. It is important to note that this is a sample portfolio and may not be suitable for everyone.
Portfolio Review and Rebalancing
Regularly reviewing and rebalancing an investment portfolio is crucial for maintaining its intended risk profile and achieving financial goals. This involves periodically assessing the performance of each asset class, adjusting allocations as needed to align with the investor’s risk tolerance and long-term objectives. For instance, if one asset class significantly outperforms others, rebalancing might involve selling a portion of the overperforming asset and reinvesting the proceeds in underperforming assets to restore the target allocation.
The frequency of rebalancing can vary, but a yearly review is generally recommended. This process helps to maintain the desired level of diversification and prevent excessive exposure to any single asset class. A disciplined rebalancing strategy helps to capitalize on market fluctuations and to maintain a consistent level of risk.
Understanding Fees and Expenses

Investing, even in low-risk options, inevitably involves some costs. Understanding these fees is crucial for maximizing your returns and ensuring your investment strategy aligns with your financial goals. Ignoring fees can significantly erode your investment growth over time, especially with smaller initial investments. Therefore, a thorough understanding of fee structures across different low-risk investment vehicles is paramount.
Types of Investment Fees
Various fees can impact the profitability of low-risk investments. These fees are often presented as percentages or fixed amounts, and understanding their implications is essential for making informed investment decisions. Failing to account for these fees can lead to a miscalculation of potential returns.
Fee Structures Across Low-Risk Investments
High-yield savings accounts and money market accounts typically have minimal fees, often charging only if you fall below a minimum balance or make excessive withdrawals. Certificates of Deposit (CDs) usually have no fees, although early withdrawal penalties can be substantial. Government bonds and Treasury bills generally have low transaction costs, but brokerage fees may apply if purchased through a broker.
Series I Savings Bonds have no transaction fees but do have purchase limits. The fees associated with each investment vehicle should be carefully weighed against the potential returns. For example, a higher-yielding CD might have a higher early withdrawal penalty, while a lower-yielding account might offer greater flexibility.
Strategies for Minimizing Investment Fees
Minimizing investment fees involves careful selection of investment vehicles and brokers. Choosing online brokerage accounts often reduces transaction costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar brokers. Understanding the fee schedule of your chosen financial institution is critical. Negotiating lower fees with your broker, especially for larger investments, is also a possibility. Finally, consolidating investments into fewer accounts can streamline management and potentially reduce overall fees.
For example, managing all your investments through a single, low-fee brokerage account simplifies tracking and reduces potential administrative charges.
Common Investment Fees and Their Implications
The following are common investment fees and their impact on investment returns. Understanding these fees is vital for making sound investment choices.
- Management Fees: Charged by mutual funds and other managed investment accounts. These fees can significantly reduce overall returns over time. A high management fee of 2% annually, for instance, can eat into profits substantially over several years.
- Transaction Fees: Charged for buying or selling investments. These fees can be particularly significant for frequent traders, but are usually minimal for low-risk, buy-and-hold strategies.
- Account Maintenance Fees: Charged by some financial institutions for maintaining an investment account. These fees are usually avoidable by maintaining a minimum balance.
- Early Withdrawal Penalties: Applied to CDs and some other investments if you withdraw funds before maturity. These penalties can significantly reduce your returns. A 6-month early withdrawal penalty on a CD, for example, might wipe out a substantial portion of accrued interest.
- Brokerage Fees: Charged by brokers for facilitating investment transactions. Online brokers often have lower fees than traditional brokers.
The Role of Inflation in Low-Risk Investments
Inflation, the persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy, significantly impacts the real return of investments. Understanding this impact is crucial for beginners navigating the world of low-risk investments, as it directly affects the purchasing power of your savings. While low-risk investments offer stability and capital preservation, they often don’t outpace inflation, meaning your money might lose its value over time.Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money.
If the inflation rate is 3%, an investment that yields 2% annually actually loses 1% of its purchasing power each year. This means you can buy less with your investment’s returns than you could have a year earlier. This is because the money you earn in interest doesn’t keep pace with the rising prices of goods and services.
This phenomenon is especially pronounced during periods of high inflation, such as the inflationary period of the 1970s in the United States or more recent inflationary spikes seen globally in 2022-2023.
Inflation’s Impact on Low-Risk Investment Returns
Analyzing historical data reveals a clear relationship between inflation and the returns of various low-risk investment vehicles. For example, during periods of high inflation (e.g., the late 1970s), the returns on savings accounts and government bonds often lagged behind the inflation rate, resulting in a net loss in purchasing power. Conversely, during periods of low inflation (e.g., the early 2000s), these same investments may have provided a positive real return.
Comparing the historical performance of low-risk investments (like savings accounts and CDs) with corresponding inflation rates reveals that while they provide a degree of safety, their returns often do not consistently outpace inflation, especially in periods of higher inflation. This necessitates strategic planning to mitigate this risk.
Strategies for Inflation Protection in Low-Risk Portfolios
Several strategies can help mitigate the impact of inflation on low-risk investment portfolios. These strategies are not without risk, but they offer a better chance of preserving purchasing power compared to relying solely on low-yield instruments.A diversified approach incorporating a mix of low-risk and inflation-hedging assets is often recommended. For instance, while a high-yield savings account provides liquidity and safety, it might not protect against inflation.
Adding Series I bonds, which adjust their interest rate based on inflation, can offer a degree of protection against inflation’s eroding effects. Furthermore, consider a small allocation to Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), which are government bonds that adjust their principal based on inflation, providing a more robust hedge. While TIPS are not strictly “low-risk” in the sense of their price fluctuating, their inflation protection makes them a valuable addition to a portfolio aiming to maintain purchasing power over the long term.
The inclusion of these instruments should be carefully considered based on one’s individual risk tolerance and investment goals.
Illustrative Example: Building a $5,000 Low-Risk Portfolio
Constructing a diversified low-risk portfolio with a $5,000 investment requires careful consideration of asset allocation to minimize risk while aiming for modest returns. This example demonstrates a possible approach, emphasizing the importance of spreading investments across different asset classes to mitigate potential losses. Remember that past performance is not indicative of future results, and individual circumstances should always guide investment decisions.
Consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance.This example allocates the $5,000 across several low-risk investment vehicles, reflecting a conservative approach suitable for beginners. The goal is to preserve capital while achieving a small, steady return above inflation. This strategy prioritizes stability over potentially higher, but riskier, returns.
Asset Allocation Strategy
The sample portfolio employs a diversified strategy, spreading the $5,000 across four asset classes. This diversification aims to reduce the overall risk. If one asset underperforms, the others may offset those losses, providing a cushion against significant portfolio decline. The specific allocation percentages are chosen for their balance between risk mitigation and potential growth within a low-risk framework.
| Asset Class | Amount | Percentage | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Yield Savings Account | $1,500 | 30% | Provides readily accessible liquidity and a modest return. |
| Certificates of Deposit (CDs) | $1,500 | 30% | Offers a fixed interest rate for a specified term, providing predictable returns. |
| Government Bonds (Treasury Bills) | $1,000 | 20% | Backed by the government, these bonds offer low risk and stable returns. |
| Series I Savings Bonds | $1,000 | 20% | Inflation-protected bonds offering a return that adjusts with inflation. |
High-Yield Savings Account Role
A high-yield savings account serves as the portfolio’s liquid component. The $1,500 allocated here provides easy access to funds for emergencies or unexpected expenses. While the return may not be exceptionally high, the accessibility and FDIC insurance (up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank) make it a crucial element of a low-risk strategy. The liquidity ensures that funds are readily available when needed without incurring penalties.
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) Role
The $1,500 investment in CDs provides a predictable return over a fixed period. CDs offer higher interest rates than savings accounts, but the money is locked in for the term, typically ranging from a few months to several years. Choosing a CD maturity date aligns with your financial goals. For example, a shorter-term CD might be suitable for funds needed in the near future, while longer-term CDs can be used for longer-term financial objectives.
FDIC insurance applies to CDs as well, providing security for the invested capital.
Government Bonds (Treasury Bills) Role
Government bonds, particularly Treasury Bills, are considered among the safest investments. The $1,000 invested here provides a low-risk, stable return backed by the full faith and credit of the government. Treasury Bills are short-term debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury, typically maturing in less than a year. Their low risk makes them an ideal component of a conservative portfolio.
The returns are generally modest, but the extremely low risk is a significant advantage.
Series I Savings Bonds Role
Series I savings bonds are unique in their inflation protection. The $1,000 invested here offers a combination of a fixed rate and an inflation-adjusted rate, shielding the investment from the erosion of purchasing power due to inflation. This feature is particularly valuable in times of rising inflation, ensuring the real value of the investment is preserved. While the initial return might be modest, the inflation adjustment provides a significant long-term benefit.
These bonds have a minimum holding period, so accessing the funds before maturity may result in penalties.
Building a low-risk investment portfolio for beginners in 2024 doesn’t require complex financial expertise. By carefully considering your risk tolerance, understanding the features of different low-risk investment vehicles, and employing a diversified approach, you can lay a solid foundation for long-term financial success. Remember that consistent contributions and regular portfolio reviews are crucial for maintaining a healthy financial trajectory. While these options prioritize capital preservation, it’s vital to remember that no investment is entirely without risk.
However, by making informed choices based on sound financial principles and a clear understanding of your goals, you can navigate the world of investing with confidence and achieve sustainable growth.
Clarifying Questions
What is the difference between a high-yield savings account and a money market account?
While both offer FDIC insurance and higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts, money market accounts often require higher minimum balances and may offer check-writing or debit card access, features not typically found in high-yield savings accounts.
Are Series I bonds a good investment during periods of high inflation?
Yes, Series I bonds offer inflation protection. Their interest rate is composed of a fixed rate and an inflation rate, ensuring that your investment’s purchasing power is better protected than with fixed-rate investments during inflationary periods.
How often should I rebalance my low-risk investment portfolio?
A general guideline is to rebalance your portfolio annually or semi-annually, adjusting asset allocation to maintain your desired risk level and asset distribution. Market fluctuations may necessitate more frequent adjustments.
What are some common investment fees I should be aware of?
Common fees include management fees (for managed accounts), transaction fees (for buying and selling investments), and early withdrawal penalties (for CDs). Understanding these fees is crucial for maximizing your returns.
Can I lose money in a low-risk investment?
While low-risk investments aim to minimize losses, the possibility of losing some purchasing power due to inflation exists. Furthermore, some investments, even low-risk ones, may have minor fluctuations in value. However, the likelihood of significant losses is generally lower compared to higher-risk investments.


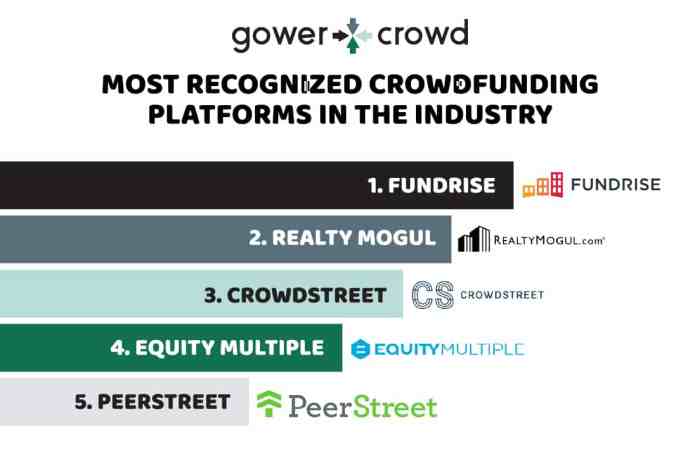














 However, the age of the property will be a crucial factor. You can get pleasure from tax deductions beneath section 80C of the IT act. Investment property tax deductions in Sydney are an necessary factor for you to consider in case you are residing right here. One among the most important thing that you simply need to know is that the mortgage is lent in opposition to the worth of the property. That is primarily as a consequence of the explanation that tax handling of bills incurred in any sort of property is different for rental and resale properties. As you put money into the true estate market you’ll discover that coming throughout scorching investment properties is as much about doing all of your due diligence as it’s about rubbing shoulders with lady luck. As a result of structural complexity of real property crowdfunding, and new changes in SEC laws, these investment opportunities may work very effectively for some buyers and may not for others. Note that drawdown constraints may result implicitly from the structure of hedge fund manager’s incentives by means of the high-water mark provision-see e.g. Guasoni. But the end result can be fruitful. Likely, both your personal and enterprise credit score scores can be thought-about to find out your creditworthiness, in addition to your debt-to-revenue ratio. Th is po st was done with GSA Cont ent Genera tor DEMO !
However, the age of the property will be a crucial factor. You can get pleasure from tax deductions beneath section 80C of the IT act. Investment property tax deductions in Sydney are an necessary factor for you to consider in case you are residing right here. One among the most important thing that you simply need to know is that the mortgage is lent in opposition to the worth of the property. That is primarily as a consequence of the explanation that tax handling of bills incurred in any sort of property is different for rental and resale properties. As you put money into the true estate market you’ll discover that coming throughout scorching investment properties is as much about doing all of your due diligence as it’s about rubbing shoulders with lady luck. As a result of structural complexity of real property crowdfunding, and new changes in SEC laws, these investment opportunities may work very effectively for some buyers and may not for others. Note that drawdown constraints may result implicitly from the structure of hedge fund manager’s incentives by means of the high-water mark provision-see e.g. Guasoni. But the end result can be fruitful. Likely, both your personal and enterprise credit score scores can be thought-about to find out your creditworthiness, in addition to your debt-to-revenue ratio. Th is po st was done with GSA Cont ent Genera tor DEMO !